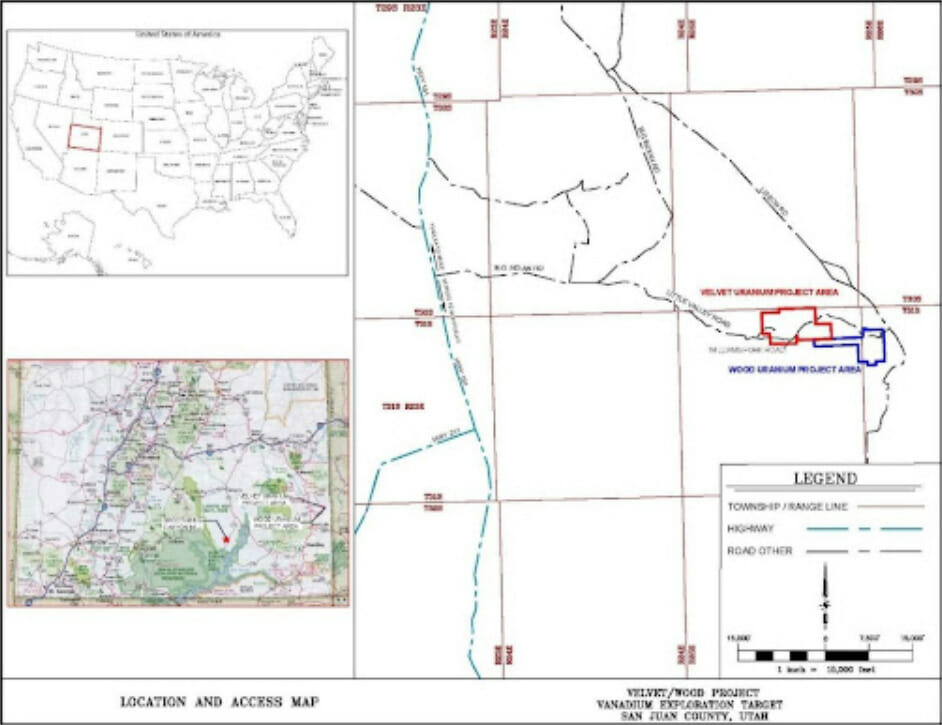
The Velvet area is located in San Juan County, Utah, approximately 31 miles from Monticello, Utah, in Township 31 South, Range 25 East, Sections 2, 3, 4 and 10, at Latitude 38o 07’ 00” North and Longitude 109º 09’ 00” West. The Wood area is located in Township 31 South, Range 26 East, Sections 6 and 7 and Township 31 South, Range 25 East, Sections 1, 11, and 12 at Latitude 38o 08’ 00” North and Longitude 109o 06’ 00” West. Project ownership includes unpatented mining claims and a State of Utah mineral lease as shown on Figure 4.1, totaling approximately 2,166 acres related to the Velvet and Wood mine areas as shown on Figure 4.1.
Velvet-Wood Project
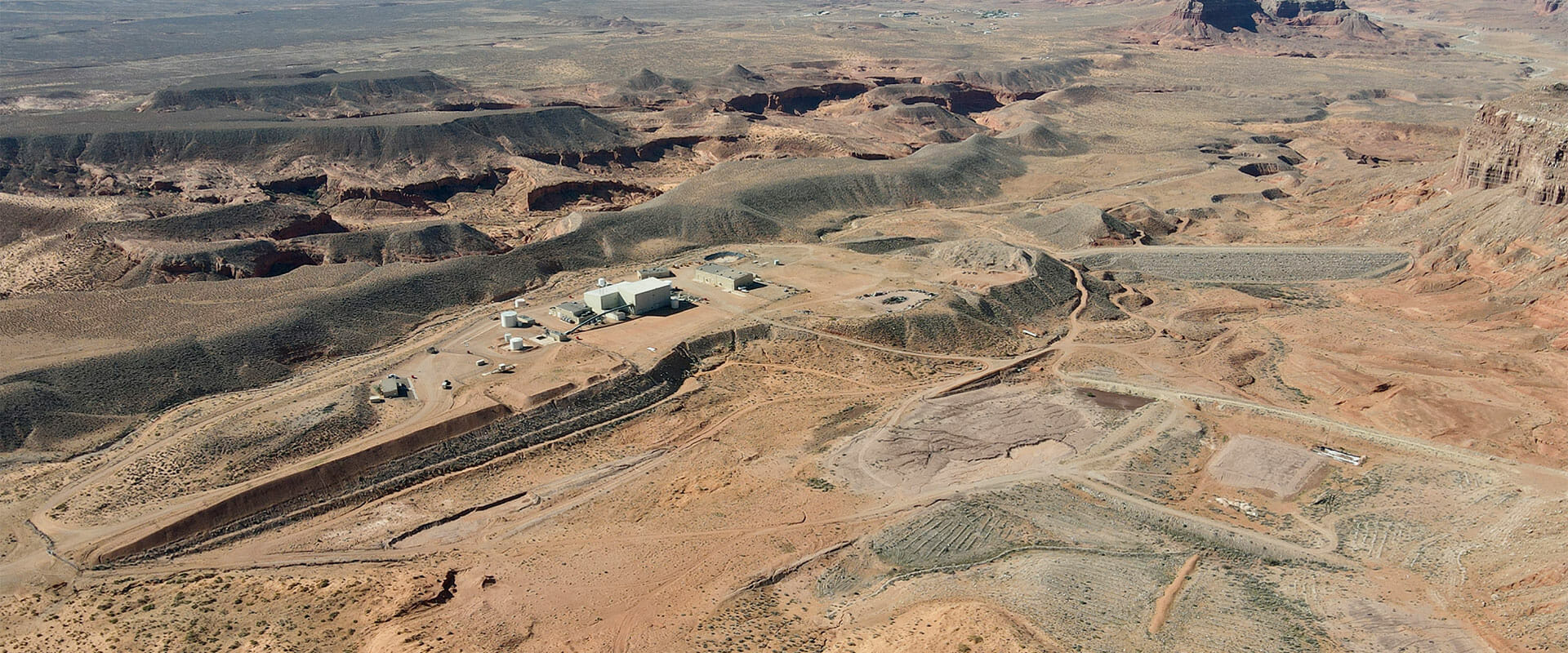

Anfield’s Most Advanced Uranium/Vanadium Asset
Acquired alongside the Shootaring Canyon Mill in 2015, this project holds significanthistorical mineral resources. With measured and indicated categories containing 4.6 million pounds ofeU3O8 (0.285% grade) and inferred categories holding 552,000 pounds of eU3O8 (0.320% grade) and7.3Mlbs of V2O5 (0.404% grade), Velvet-Wood demonstrates its potential.
From 1979 to 1984, the project yielded significant results, recovering around 4 million pounds of U3O8and 5 million pounds of V2O5 from mining approximately 400,000 tons of ore with grades of 0.46%U3O8 and 0.64% V2O5. The Velvet mine retains underground infrastructure, including a 3,500 ft long,12′ x 9′ decline to the ore body. As Anfield Energy’s most advanced uranium asset, Velvet-Woodsignifies a potential near-term path to uranium and vanadium production. Join us as we unlock theproject’s full potential.
Preliminary Economic Assessment:
Download Full Report
Highlights
The most advanced asset in Anfield’s uranium portfolio.
Between 1979 and 1984 approximately 400,000 tons of ore were mined from the Velvet deposit at average grades of 0.46% U3O8 and 0.64% V2O5 (recovering approximately 4 million pounds of U3O8. and 5 million pounds of V2O5).*
Some underground infrastructure is already in place at the Velvet mine, including a 3,500 ft long, 12’ x 9’ decline to the ore body.
The historical mineral resources of the combined Velvet and Wood mines have been estimated to comprise 4.6 million pounds of U3O8 at an average grade of 0.285% U3O8 (measured and indicated resource), along with 638,500 pounds of U3O8 at an average grade of 0.173% U3O8 and 4.7 million pounds of V2O5 at an average grade of 0.404% V2O5 (inferred resource).**
* Source: Lisbon Valley, Utah’s Premier Uranium Area, A Summary of Exploration and Ore Production, William L. Chenoweth, Utah Geological and Mineral Survey Open-File Report 188, July 1990.
**Source: 2023 PEA, The PEA completed for the combined Velvet-Wood and Slci Rock projects has been authored by Douglas L. Beahm, P.E., P.G. Principal Engineer, of BRS Inc., Terence P. (Terry) McNulty, P.E., D. Sc., of T.P. McNulty and Associates Inc.
See “Summary of Uranium One Conventional Uranium Asset Transaction” for more information regarding the status of the properties described in this section.

Table 1: Velvet-Wood Project Historic Resource
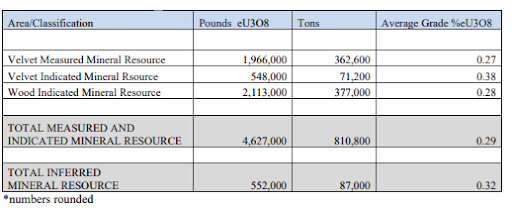
Source: Velvet-Wood Mine Uranium Project, San Juan County, Utah USA 43-101 Mineral Reserve and Resource Report, Author: BRS Inc.; Date: 11/14/2014
Location
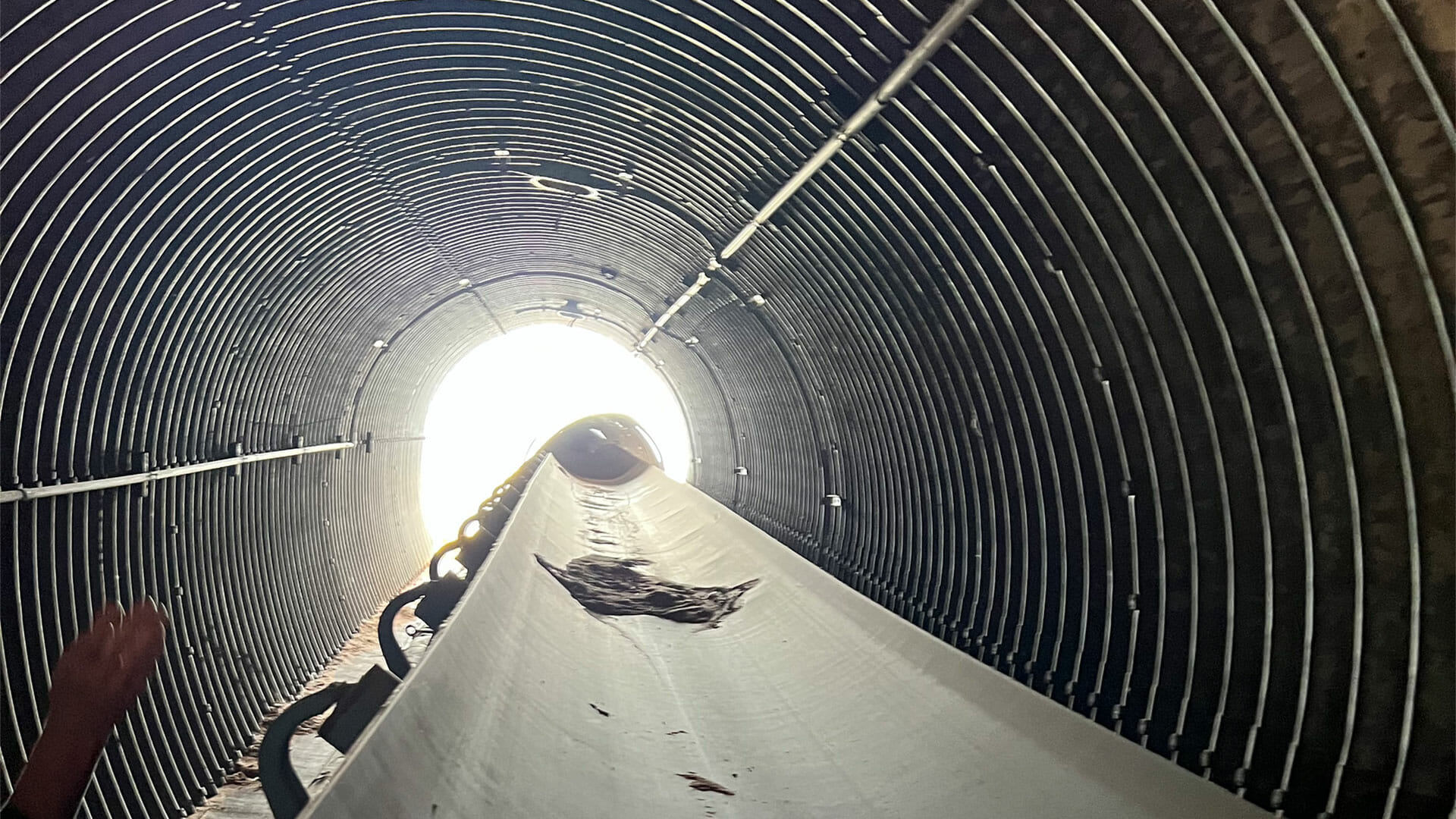

History
The ownership history of the Velvet-Wood mineral holdings has undergone changes over time. Anfield Energy acquired the Velvet-Wood mine and other conventional uranium assets from Uranium One in August 2015.
The Velvet-Wood Uranium and Vanadium Project is comprised of two separate areas that were historically owned by different companies. The Velvet area was previously held by Atlas Minerals, who conducted mining operations on parts of the mineralization. Simultaneously, the Wood area was owned by Uranerz during a similar time period. Uranerz conducted drilling activities from 1985 to 1991, with 120 rotary holes drilled, and outlined the current Wood mineral resource area (Chenoweth, 1990). However, it is important to note that the Wood area described in this report was drilled but not mined.
Geology
The Velvet-Wood project is situated within the Lisbon Valley uranium district, which holds the distinction of being the largest uranium-producing district in Utah. From 1948 to 1988, the Lisbon Valley, also known as the Big Indian Wash District, produced five times more uranium than any other district in Utah. The total production during this period amounted to an impressive 77,913,378 pounds of U308 (uranium concentrate) at an average grade of 0.30% U308 (Chenoweth, 1990).
In the Velvet and Wood areas of the project, uranium mineralization is found within sandstone units of the Cutler Formation. These sandstones are fluvial arkose that have undergone a process called bleaching. The mineral deposits within the project are irregular and take the form of tabular bodies (Denis, 1982). They are located at the base, top, or in close proximity to pinch-outs (narrowing) of the sandstone bodies (Campbell and Mallory, 1979). The primary productive zone within the Cutler Formation occurs near the unconformity, which is the boundary, between the Cutler Formation and the overlying Chinle Formation.
Permitting
Permitting for Velvet-Wood mining operations requires various approvals from the state of Utah Division of Oil, Gas and Mining (DOGM) and the US Bureau of Land Management (BLM). There is an existing Large Mine permit for the Velvet Mine which will need to be updated and revised.
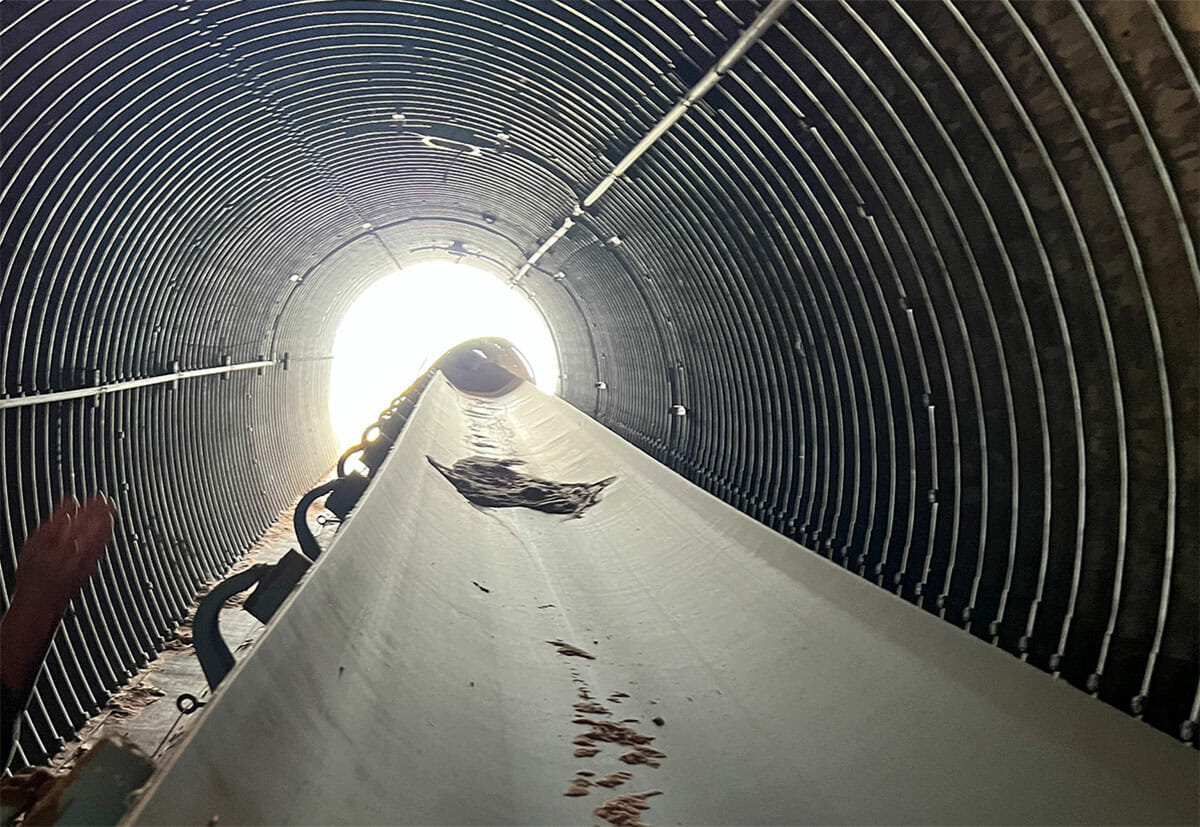

Access
Portions of the Velvet deposit have undergone previous mining activities, which involved accessing the mineralization through a portal and decline. The mine entrance has since been closed off with backfill, but has the potential to be reopened for future operations. The Velvet portal can be reached via well-maintained roads, starting with the Big Indian Road. This road is a paved surface road that branches off from U.S. Highway 191, approximately 19 miles north of Monticello, Utah, or 34 miles south of Moab, Utah.
The Big Indian Road extends eastward and forms a loop with the Lisbon Road, serving properties in the Lisbon Valley area. Another road, San Juan County Road 112 (Williams Fork), branches off from the Big Indian Road about 5.5 miles east of its intersection with Highway 191. There is a private access road that connects with County Road 112 around 6 miles southeast of its intersection with the Big Indian Road. Travelling along these roads for about one mile northeast will lead to the Velvet Mine portal. The described route can be navigated using a 2-wheel drive vehicle on existing county and/or two-track roads. The project is located approximately 10 miles south of La Sal, Utah. Most transportation for the project will be facilitated by commercial trucks. Access to exploratory drill sites and vent locations is provided through existing roads connected to the main access point at the Velvet portal and the Lisbon Road.
The Wood mine area is situated approximately 3 miles east of Velvet and can be accessed via County Road 112. It is also accessible from the east using the Lisbon Valley Road and County Road 112.
Utah

The PEA for Velvet-Wood/Slick Rock was authored by Douglas L. Beahm, P.E., P.G. Principal Engineer, Harold H. Hutson, P.E., P.G. and Carl D. Warren, P.E., P.G., of BRS Inc., Terence P. (Terry) McNulty, P.E., D. Sc., of T.P. McNulty and Associates Inc. (May 6, 2023). Mineral resources are not mineral reserves and do not have demonstrated economic viability in accordance with CIM standards. GT cut-off varies by locality from 0.25%-0.50%.